KYC and AML compliance: A comprehensive guide to detecting money laundering
Money laundering poses a major risk in today's economy. Discover the different types of money laundering, the warning signs of the practice, and how regulatory compliance addresses the problem – with this comprehensive guide.

Maksim Afanasjev
Introduction
Money laundering is a growing global threat, enabling financial crime and undermining the integrity of legitimate financial systems and financial institutions. It facilitates illicit activities, such as drug trafficking and illegal activity, through tactics like shell companies, cash transactions, and electronic money to disguise dirty money as clean money. Criminals also exploit sectors like real estate to move illicit funds, further complicating the fight against financial crime.
As criminals develop more sophisticated laundering tactics, businesses must strengthen their Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance efforts and implement effective money laundering controls to prevent illegal activity. KYC compliance plays a crucial role in identifying and verifying customers in the financial services sector, helping prevent the flow of dirty money into legitimate financial systems.
An effective AML program encompasses measures like KYC and emphasizes the legal and financial consequences of failing to address money laundering.
This guide covers money laundering trends, key AML regulatory frameworks like the Financial Action Task Force and Bank Secrecy Act, the role of AI-powered identity verification in compliance, and case studies on how Veriff’s solutions prevent money laundering in various sectors.
What is money laundering?
Money laundering is a technique criminals use to cover their financial tracks after they illegally obtain money from an illegitimate source.
Profits gained from criminal activity are often referred to as “dirty money.” This is because the money is directly linked to the crime and can be traced. Due to this, criminals need to “clean” the money so that it appears legal and can be used for investments.
For money laundering to be “successful,” the dirty money must enter the financial system. So, how do banks prevent money laundering? The answer is anti-money laundering (AML) compliance.
AML requirements are a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for businesses operating in various jurisdictions. Organizations must establish their own AML policies that adhere to local regulations, including customer due diligence and the implementation of transaction monitoring systems.
Definition and examples of money laundering
Money laundering is the process of disguising the origin of illicit funds to make them appear legitimate. It involves concealing or disguising the true source of money obtained through illegal activities, such as drug trafficking, corruption, or terrorism, and integrating it into the legal financial system.
Types of money laundering
Money laundering can take various forms, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common types include:
- Traditional Money Laundering: Involves the physical movement of cash or other valuables to disguise their origin. This can include smuggling cash across borders or using cash-intensive businesses to legitimize illicit funds.
- Digital Money Laundering: Utilizes digital technologies, such as cryptocurrencies or online payment systems, to launder money. This method leverages the anonymity and speed of digital transactions to obscure the source of funds.
- Trade-Based Money Laundering: Involves the use of international trade to disguise the origin of illicit funds. This can include over- or under-invoicing goods and services, or using complex trade transactions to move money across borders.
- Real Estate Money Laundering: Involves the use of real estate transactions to launder money. Criminals may purchase properties with illicit funds and then sell them to integrate the money into the legal financial system.
Understanding these different types of money laundering helps financial institutions implement targeted AML programs to detect and prevent such activities.
Consequences of money laundering
Money laundering has significant consequences for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. Some of the key consequences include:
- Financial losses: Money laundering can result in substantial financial losses for individuals and businesses. This includes direct losses from fraud and indirect costs such as fines and regulatory penalties.
- Damage to reputation: Being associated with money laundering can severely damage a person’s or business’s reputation. This can lead to loss of customer trust, decreased business opportunities, and long-term reputational harm.
- Legal consequences: Money laundering is a criminal offense and can result in severe legal consequences, including fines, imprisonment, and other penalties. Financial institutions found to be non-compliant with AML regulations may face significant legal repercussions.
- Threat to national security: Money laundering can be used to finance terrorism and other threats to national security. By disguising the origin of funds, criminals can support activities that undermine national and global security.
These consequences highlight the importance of robust AML compliance programs to protect financial institutions and society from the risks associated with money laundering.
Understanding money laundering techniques
Before you learn how to detect money laundering and address compliance requirements, you must first understand how it works, including the techniques employed by criminals. A robust KYC process is essential in compliance with financial regulations, as it helps organizations verify customer identities, assess risks, and maintain compliance with AML regulations.
Money laundering involves three key stages: placement, layering, and integration.
Placement
The placement stage refers to how and where illegally obtained funds are introduced into the financial system. Methods used by fraudsters include:
- Making payments to cash-based businesses.
- Making payments for false invoices.
- Depositing small amounts of money (below the AML threshold) into bank accounts or credit cards.
- Moving money into trusts and offshore companies that hide owner identities.
- Using foreign bank accounts.
- Aborting transactions shortly after funds are lodged with a lawyer or accountant.
Layering
The layering stage refers to how criminals separate illegally obtained funds from their source. This often involves complex financial transactions designed to disguise the origins and ownership of the funds. The goal is to make it difficult for AML investigators to trace the transactions back to their illicit origins.
Integration
The integration phase happens when the laundered funds re-enter the economy in what appear to be legitimate business or personal transactions. Common methods include purchasing real estate, luxury assets, and high-value goods.

Red flags of money laundering
Recognizing the warning signs of money laundering is crucial for compliance officers and financial institutions. Ongoing compliance is essential to maintain adherence to KYC and AML regulations, ensuring that policies and procedures are regularly updated to adapt to changing regulatory landscapes. Common red flags include:
- Unusual financial activity that deviates from a customer’s normal transaction patterns.
- Large cash deposits with no clear justification for their origin.
- Evasive or defensive responses when questioned about transactions.
- Discrepancies in provided information or documentation.
- Large investments made by third parties without a clear explanation.
- Increasingly complex financial transactions with no apparent business purpose.

The impact of money laundering on businesses
Money laundering affects businesses in multiple ways:
- Financial losses due to fraud, fines, and regulatory penalties.
- Reputational damage from non-compliance and association with financial crime.
- Regulatory scrutiny, including audits, investigations, and possible sanctions.
- Operational inefficiencies from outdated AML procedures and manual compliance checks
Key AML compliance frameworks
Regulations play a crucial role in enforcing AML compliance worldwide. AML laws and KYC regulations are critical in combating financial crime and ensuring organizations' compliance. Some key frameworks include:
Global:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidelines being a guiding lighthouse for many countries’ AML frameworks.
United States:
European Union:
United Kingdom:
Understanding AML regulations
Overview of AML regulations and laws
Anti-money laundering (AML) regulations are critical for protecting the global financial system from illicit activity and ensuring compliance with international standards. These frameworks, which countries often align with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidelines, equip institutions to detect and prevent money laundering and related crimes effectively.
Globally, AML enforcement adheres to FATF recommendations, with national agencies adapting regulations to address evolving threats. Financial institutions are expected to continuously refine their AML frameworks, leveraging advanced technology and robust procedures to stay ahead of emerging risks. This approach underscores a commitment to security, trust, and compliance in a rapidly changing regulatory landscape.
In the United Kingdom, AML compliance is driven by the Proceeds of Crime Act (POCA) 2002 and the Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing, and Transfer of Funds (Information on the Payer) Regulations 2017. POCA mandates both individuals and organizations to report suspicious activity and restrict the use of criminally derived funds. The 2017 regulations require financial institutions to implement customer due diligence (CDD), ongoing monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting to mitigate financial crime risk.
In the United States, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and the USA PATRIOT Act form the backbone of AML efforts. These laws enforce key measures, such as reporting transactions exceeding $10,000, conducting customer due diligence, and applying enhanced due diligence (EDD) for high-risk profiles. The emphasis is on robust record-keeping, monitoring, and identifying suspicious transactions to ensure compliance.
What can businesses do to prevent money laundering?
- Conduct thorough KYC (Know Your Customer) processes and due diligence to verify clients' identity and assess potential associated risks. This helps prevent illegal activities, such as money laundering.
- Monitor transactions carefully for red flags, such as unusual payment patterns, large cash deposits, or transactions in high-risk regions. Use advanced software and manual reviews to catch suspicious activities.
- Train employees regularly on AML risks and compliance procedures. Ensure they understand how to identify and respond to potential threats, keeping your organization compliant and secure.
- Report any suspicious activities promptly to the appropriate authorities, such as financial regulators, to meet legal requirements and support broader efforts to combat financial crime.
How AI-powered Identity Verification strengthens AML compliance
Veriff combines powerful fraud detection with lightning-fast identity verification, delivering accurate results in just six seconds. Supporting over 12,000 identity documents from 230+ countries and territories, Veriff makes global onboarding seamless, with a localized interface in 48 languages to enhance user experience and drive conversions.
Traditional AML processes are often inefficient—manual, error-prone, and time-intensive. As regulations grow more complex, businesses must navigate diverse compliance requirements across jurisdictions. Veriff streamlines this challenge by integrating its advanced IDV solution into KYC, CIP, and Age Verification workflows. Our technology ensures compliance on both local and global scales, while delivering a secure, seamless user experience.
With a global presence and deep expertise in international compliance, Veriff streamlines verification processes across borders, giving you the confidence to scale your business internationally. From adhering to AML and KYC regulations to safeguarding data privacy, Veriff helps you build trust, secure user interactions, and create safer online environments.
Using AI-driven identity verification during onboarding, Veriff ensures every customer is a real person. Our advanced KYC processes form the backbone of anti-money laundering (AML) and customer due diligence (CDD) frameworks. Risk scoring systems evaluate customer profiles for AML compliance, while continuous monitoring adjusts risk profiles based on user behavior. With Veriff, you can trust that your compliance efforts are both precise and reliable, empowering your business to thrive in a rapidly evolving digital world.
Book a consultation with Veriff
With a comprehensive understanding of money laundering detection and criminal tactics, implement robust processes to shield your business from becoming a target. Leverage advanced strategies and industry-leading practices to ensure your organization remains secure and trustworthy.
The starting point for AML compliance is online identity verification. After all, when welcoming a new customer, you need to make sure that your new customer is genuine person, within your organization’s risk profile, and not subject to any sanctions. Thankfully, our identity verification and AML Screening solutions help you towards meeting your compliance and KYC requirements.
Veriff’s AI-powered Identity Verification solutions
- AI-driven identity verification and fraud detection to support AML compliance.
- Seamless integration with KYC, Customer Due Diligence (CDD), and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) requirements.
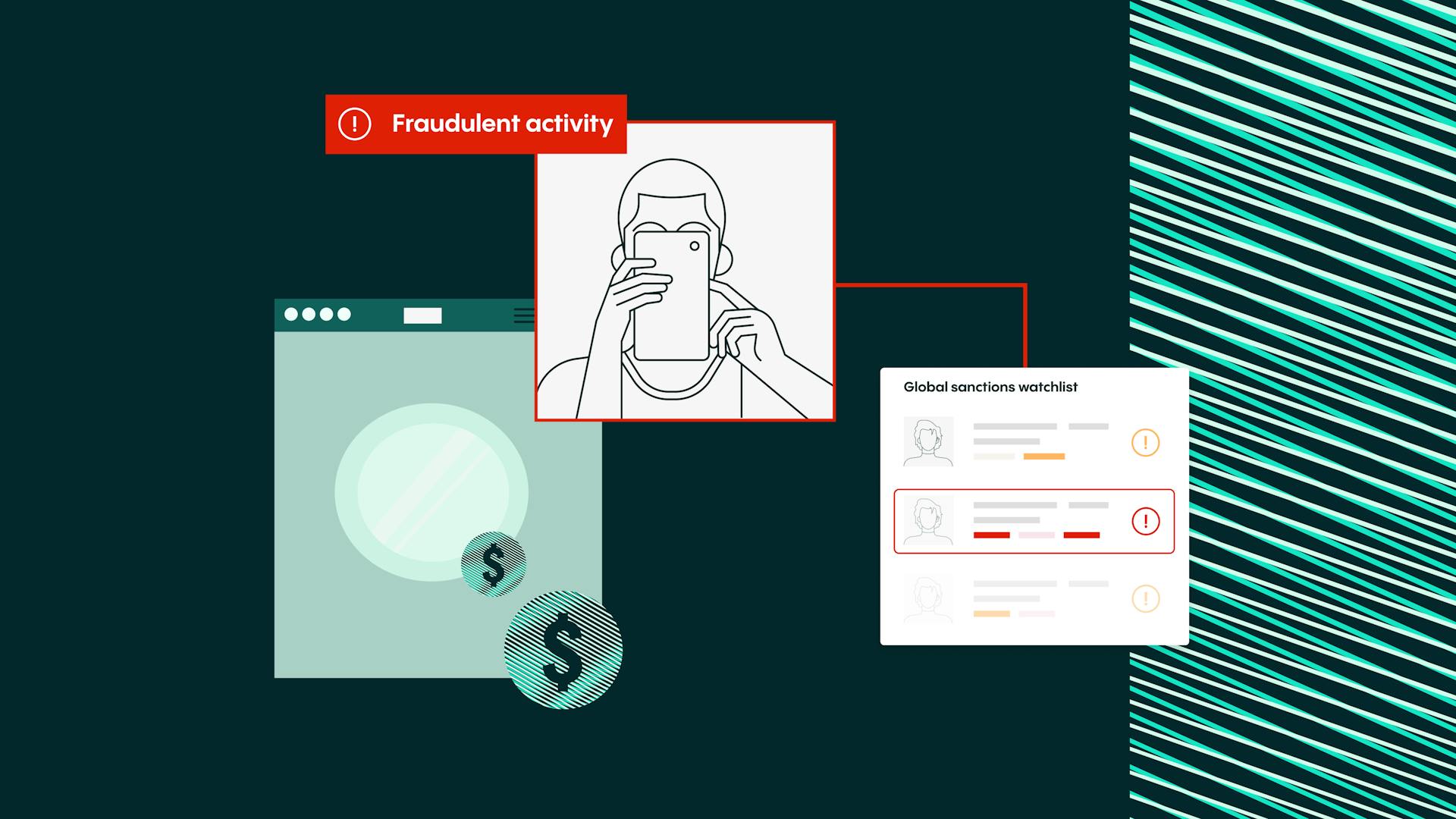
- Veriff’s AML Screening solution performs comprehensive checks against global sanctions lists and watchlists to identify and mitigate risks associated with high-risk individuals.
Real-world case study: Veriff & Comun
Comun is a digital banking platform designed for immigrant communities in the US. To ensure compliance with KYC and AML regulations, Comun integrated Veriff’s identity verification solutions, allowing it to:
- Verify identities quickly and accurately.
- Prevent fraudulent transactions and identity theft.
- Strengthen AML compliance in cross-border transactions.
“Before Veriff, the most common fraud Comun saw was identity theft. This has been almost completely solved by having the strong KYC system Veriff provides.”
Learn more
Get the latest from Veriff. Subscribe to our newsletter.
Veriff will only use the information you provide to share blog updates.
You can unsubscribe at any time. Read our privacy terms



