The importance of KYC and CDD in AML compliance: What your business needs to know
In this blog, we will explore the basis of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Customer Due Diligence (CDD) measures and how these processes support anti-money laundering (AML) functions. We will further delve into what businesses need to know and do to meet their regulatory responsibilities.

Dmytro Sashchuk
Introduction
Do you remember the last time you went physically to the bank to send money somewhere?
While many 'yes' answers may be expected, it is undeniable that nowadays opening your bank account online and sending money on its way can be done in a matter of minutes - and all from the comfort of your home. The underlying causes for such a rapid digitalization may be plenty and complex, but clearly the COVID-19 pandemic and substantial increase in the number of FinTechs have certainly contributed to us moving our money online.
Katharina Cera, Allegra Pietsch, and Andrzej Sowiński in their article prepared for the European Central Bank's “Financial Stability Review, November 2023” observe this trend by showing that “digitalization is progressing in both traditional banking and investment services”. At the same time, the same authors appropriately address the digitalization as a double-edged sword - it brings plenty of benefits while simultaneously magnifying risks to the financial systems.
As a result, tackling money laundering has become a growing concern for governments, regulators, and financial institutions worldwide. Reports indicate that money laundering cases are on the rise, as evidenced by data from Eurojust's Money Laundering Report 2022 and other global sources. According to The Business Research Company’s Anti-Money Laundering Global Market Report 2025, the market is projected to grow from $2.92 billion in 2024 to $3.39 billion in 2025, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16%.

This surge reflects an increasing emphasis on financial security and compliance, fueled by factors such as globalization, digital transactions, and stricter regulatory requirements. Government enforcement initiatives and advances in regulatory technology (RegTech) are further shaping the landscape of AML solutions.
For businesses subject to AML regulations, ensuring compliance is more critical than ever. Beyond the risk of regulatory fines, failing to implement robust compliance measures can erode customer trust—a crucial asset in the financial sector.
In this article, we aim to arm you with the most important knowledge when it comes to understanding AML obligations, specifically CDD measures and KYC procedures, their differences, and how they enable your business to ensure compliance with AML obligations.
Three fancy acronyms: what they are all about
1. Anti-money laundering obligations: where it all starts
AML refers to a framework of laws, regulations, and procedures designed to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. These obligations apply to financial institutions and other designated businesses (referred to as "obliged entities") that must identify and mitigate risks associated with financial crimes.
Core AML obligations include:
Some of the AML obligations that obliged entities need to comply with include, but are not limited to:
- Performing risk assessments;
- Designing and implementing system of policies, controls and procedures to ensure compliance;
- Designating an employee who is responsible for monitoring and facilitating compliance;
- Implementing customer due diligence process taking into account identified risks;
- Retaining customer records; and
- Filing occasional and suspicious transactions reports.
While AML principles are globally recognized, implementation varies by jurisdiction. Most countries align their frameworks with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), but specific regulatory requirements may differ based on local risks.
2. Customer due diligence: an "airport security scanner" for money laundering prevention
The CDD is a two-fold concept that stands as the central element of AML compliance and is especially important for all obliged entities.
From one side, the CDD can be characterized as a set of measures that obliged entities must implement to mitigate the risks of their services being exploited for money laundering, including verifying the customer's identity, while on another side, it is also a process of continuous application of these measures.
Red flags in CDD
Red flags in CDD are warning indicators of potentially suspicious or high-risk activities. Financial institutions must be vigilant in identifying these red flags to prevent money laundering and other financial crimes. Common red flags include:
- Unusual transaction patterns.
- Inconsistent identification details.
- Transactions involving high-risk jurisdictions.
- Complex ownership structures.
- Reluctance to provide necessary information.
Recognizing these red flags is crucial for financial institutions to take appropriate action, such as conducting further investigations or reporting suspicious activities to relevant authorities. By being aware of these indicators, financial institutions can better protect themselves and their customers from financial crimes.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Enhanced Due Diligence "EDD" is a more comprehensive and in-depth form of due diligence applied to customers with a higher risk profile. Financial institutions must implement EDD for customers who are considered high-risk, such as politically exposed persons ("PEPs"), individuals from high-risk countries, or situations where there’s a significant risk of money laundering. EDD involves a thorough examination of the customer’s business and financial history, which includes:
- Obtaining additional information about the customer’s business and financial activities.
- Conducting more frequent monitoring of the customer’s account activity.
- Requiring the customer to provide additional documentation or information.
EDD is an essential component of a robust Customer Due Diligence (CDD) program. It helps financial institutions better understand the risks associated with high-risk customers, and to take appropriate measures to mitigate those risks. By implementing EDD, financial institutions can ensure they are not inadvertently facilitating money laundering.
3. Know Your Customer (KYC): The first step in CDD
KYC is a fundamental component of CDD, ensuring that businesses verify and understand their customers before engaging in transactions. It involves two primary elements:
- Identification: Collecting key details such as name, date of birth, address, and nationality.
- Verification: Cross-checking the provided information against independent and reliable sources.
KYC requirements vary by jurisdiction. For example, in the U.S., the Customer Identification Program (CIP) is an integral part of KYC, whereas in the EU, requirements differ across member states.
Without a robust KYC process, businesses cannot claim to have effective CDD measures, which are essential for full AML compliance.
It is worth stressing that compliance always starts from the smallest element, and indeed without having a proper KYC process, businesses cannot claim to have addressed CDD measures, thus not achieving AML compliance. Therefore, there is an inherent inter-relation between all elements discussed in this blog.
Regional insights: Money laundering statistics by country
It is essential to examine the statistics from various regions to gain a comprehensive understanding of money laundering trends. These statistics provide crucial insights into the scale of money laundering activities and the effectiveness of the measures implemented to combat them.
United States
Money laundering remains a critical concern in the United States. The U.S. Department of the Treasury’s 2024 National Risk Assessments on Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing, and Proliferation Financing identifies key threats, vulnerabilities, and risks within the illicit finance landscape. These reports provide updated insights into evolving risks, reaffirming the importance of addressing these challenges with precision and urgency.
The United States leads globally in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) events, with over 11,472 incidents reported—equivalent to 3.5 events per 100,000 people. Annually, approximately $300 billion is laundered within the U.S., representing 15%–38% of global money laundering activity. In 2022, U.S. authorities imposed $14 billion in penalties for AML violations, underlining the financial and regulatory risks of non-compliance.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom, ranked second in AML violations, has also experienced a rise in money laundering activity. Money laundering accounts for 27.5% of all AML events in the UK, with 1,664 recorded incidents—approximately 2.5 events per 100,000 people. More than 75% of these events are directly linked to money laundering, underscoring the ongoing challenges in mitigating this threat. To address these risks, the UK has implemented robust AML frameworks, emphasizing the identification and verification of Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBOs).
Proactive measures and adherence to stringent AML practices remain essential for mitigating these significant financial and regulatory risks.
Key steps to achieve AML compliance and mitigate risks
The obliged entities must strategically approach the necessary steps to meet their compliance with applicable AML requirements. We would like to provide some insights on which steps businesses need to consider to mitigate the risks of their service being used for AML purposes.
Gathering detailed information about customers before entering into business relationships is crucial. This process helps verify identities and assess risk profiles, ensuring compliance with AML and KYC regulations.
1. Risk assessment
Perform risk assessment and implement risk management strategies by identifying key risk metrics relevant to the business, such as customer types, product offerings, services provided, and location of operations. We encourage companies to take into account national risk assessments (some of which can be located on the FATF website). This piece of information may prove useful as obliged entities are mandated to take these assessments into account when producing their own risk assessments.
2. Effective customer due diligence measures
Completing the risk assessment and getting a thorough understanding of the applicable legal framework are underlying elements of determining the proper design of CDD measures. For example, this means understanding the applicability and scope of the US CIP requirements for US financial entities is just as important as it is for the EU financial entities to understand the requirements of the Member State where they are soliciting their services.
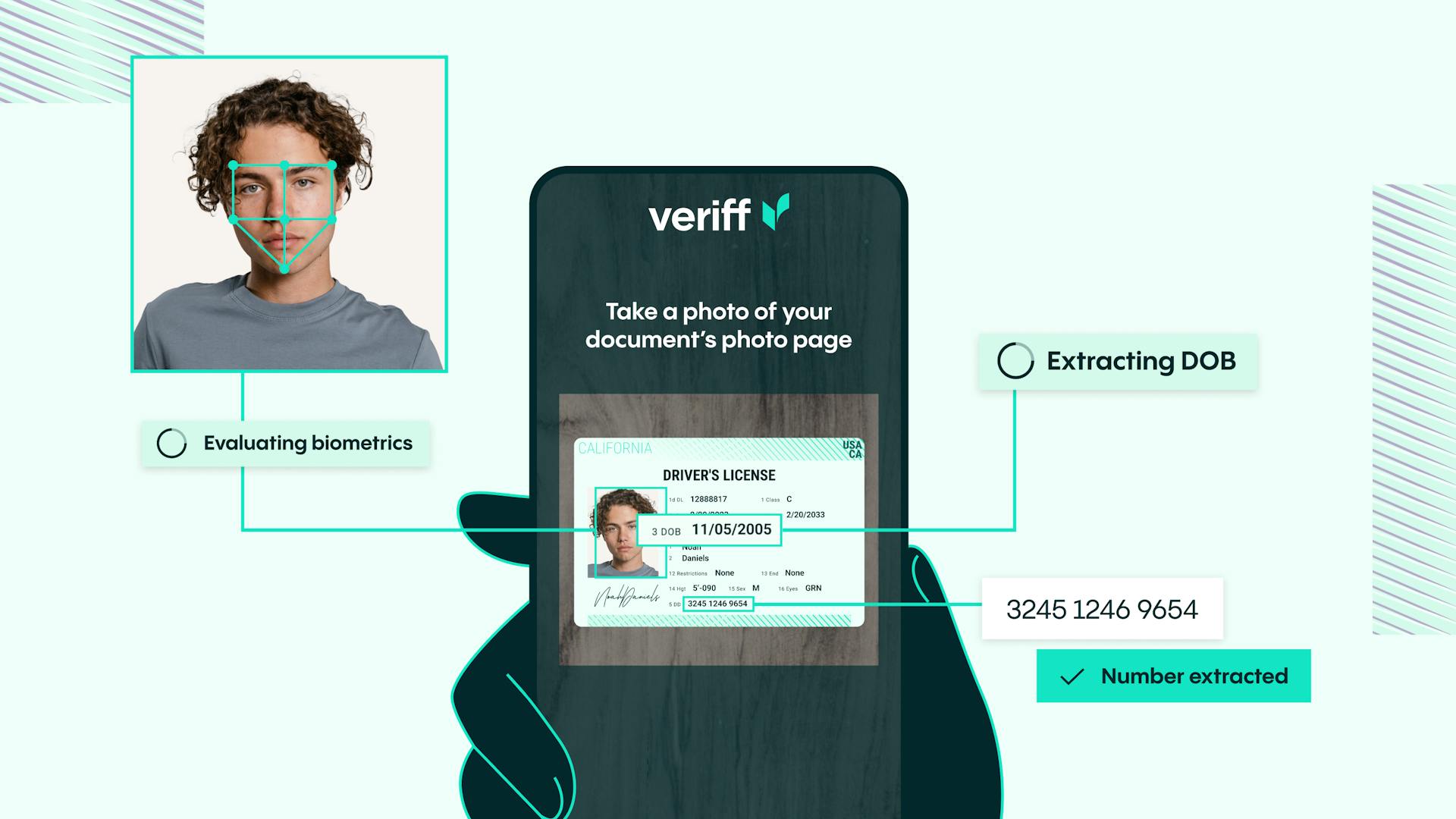
Customer due diligence solutions are essential tools for effectively addressing challenges in CDD. They help in collecting and verifying customer information through secure methods, such as identity document checks and biometric verification, to ensure the authenticity of customer identities in a digital environment.
It is no less important to implement effective measures that ensure regulatory compliance while preserving the users’ comfort. With Veriff, complying with CDD obligations doesn’t mean compromising the user experience. Veriff’s KYC onboarding solution enables you to meet regulatory compliance and onboard more genuine customers, helping to cut customer acquisition costs. With Veriff, you can also utilize optional anti-money laundering checks such as PEP and sanctions screening to make it even easier to establish and implement effective CDD measures.
3. Regulatory compliance solutions
Leveraging advanced technology such as biometric verification, which ensures secure and accurate identity authentication, and automated monitoring systems that provide real-time oversight and enhance efficiency in various processes.
4. Ongoing monitoring
Every compliant business knows that CDD is not a one-time process - it requires continious application. Monitoring users' financial behaviors and ensuring that information stays up-to-date is just as crucial as initial onboarding. Veriff's automated AML screening and ongoing monitoring solutions may be particularly useful to help keep your business compliant, mitigate risk, and keep out fraudsters while still creating a seamless experience for your genuine users.
Conclusion
AML compliance is a dynamic and essential aspect of financial security. With the increasing sophistication of financial crimes, businesses must stay ahead by implementing robust KYC and CDD measures. Compliance is not just about meeting regulations—it is about protecting customers, businesses, and the integrity of financial systems worldwide.
Real-world case study: Veriff & Comun
Comun is a digital banking platform designed for immigrant communities in the US. To ensure compliance with KYC and AML regulations, Comun integrated Veriff’s identity verification solutions, allowing it to:
- Verify identities quickly and accurately.
- Prevent fraudulent transactions and identity theft.
- Strengthen AML compliance in cross-border transactions.
Explore more
Get the latest from Veriff. Subscribe to our newsletter.
Veriff will only use the information you provide to share blog updates.
You can unsubscribe at any time. Read our privacy terms.



