What is optical character recognition? (OCR)
Today’s OCR technology is far more advanced than early versions of the technology. This is because today’s advanced solutions have the ability to deliver near-perfect OCR accuracy and can be used to automate complex document-processing workflows.
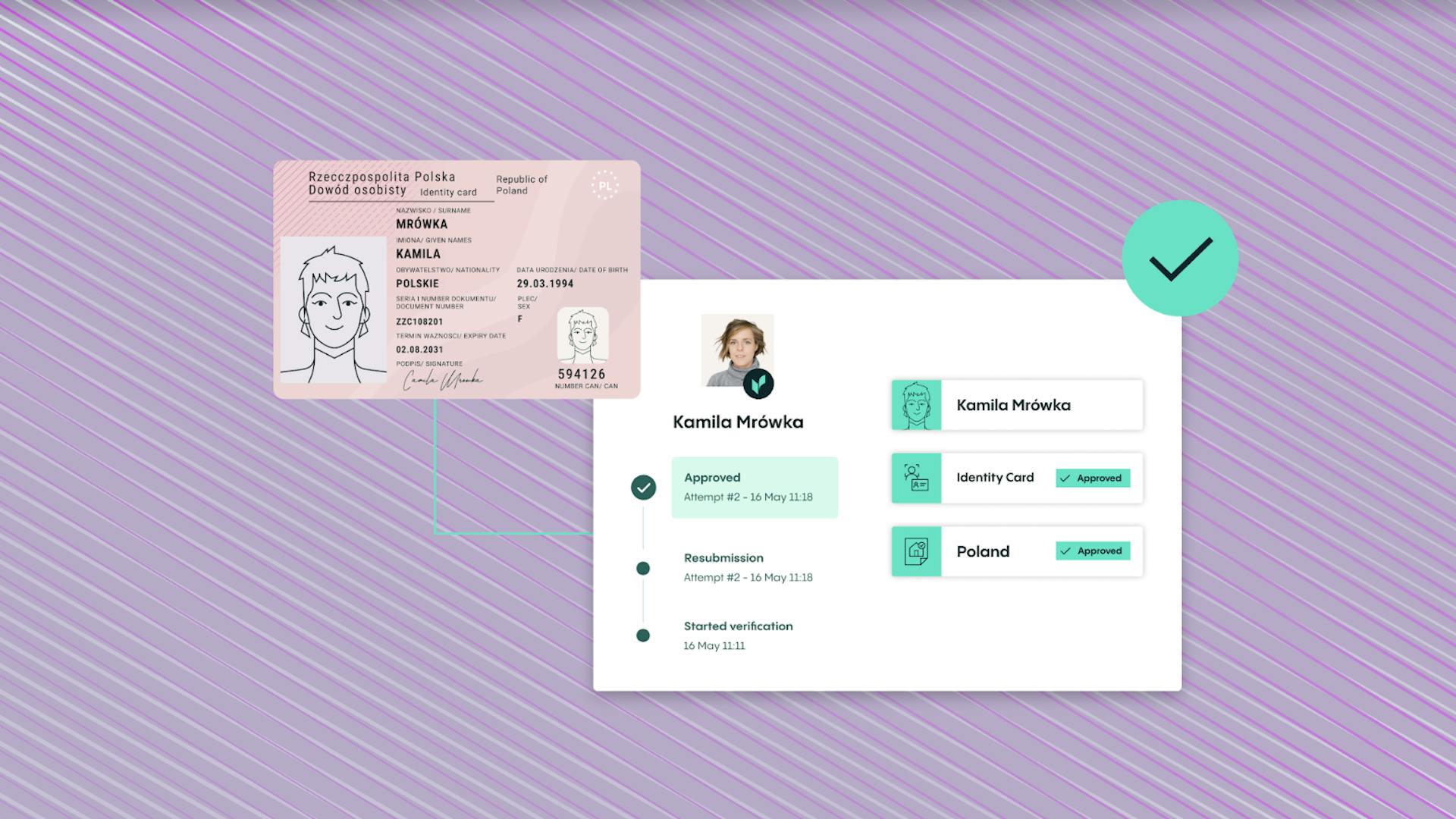
Optical character recognition (OCR) technology can save your business time, money, and effort. This is because OCR uses automated data extraction and storage capabilities that can improve the accuracy of data input and create quicker file digitization processes.
OCR is sometimes referred to as text recognition. This is because OCR programs are commonly used to extract and repurpose data from scanned documents, camera images, and image-only PDFs.
OCR enables users to access and edit the original content. But, OCR technology can be used for much more than this. For example, it can also be used to eliminate the need for manual data entry, recognize information on passports and traffic signs, and to test CAPTCHA anti-bot systems.
A History of OCR
Early forms of optical character recognition involved creating reading devices for the blind. For example, in 1914, Emanuel Goldberg developed a machine that read characters and converted them into standard telegraph code.
Following this, in the 1920s and 30s, Emanuel Goldberg developed a statistical machine for searching microfilm archives using an optical code recognition system. In 1931, he was granted a US patent number for the invention. This patent was later acquired by IBM.
A more modern form of optical character recognition was first introduced by Ray Kurzweil in 1974. His company, Kurzweil Computer Products, Inc., created an omni-font OCR product that could recognize text that had been printed in (almost) any font. Once he’d designed the product, Kurzweil decided that the best application of this technology would be a machine-learning device for the blind. As a result, the company also created a reading machine. This device was used to read text aloud in a text-to-speech format.
In 1976, the finished product was unveiled during a widely reported news conference headed by Kurzweil and the leaders of the National Federation of the Blind. Only two years later, Kurzweil began to sell a commercial version of the computer program.
After experiencing initial successes, Kurzweil Computer Products, Inc., caught the attention of XEROX, who purchased the company in 1980 and began to commercialize paper-to-computer text conversion.
Partially due to this, OCR technology gained mainstream popularity in the early 1990s, when it was primarily used to digitize historical documents and newspapers. Before OCR technology first became available, the only way to digitally format these documents and newspapers was to manually retype the text. However, this process was incredibly time-consuming and led to a number of inaccuracies and typing errors. Although these early versions of OCR technology were not perfect, they were far more accurate than humans and saved a great amount of time.
Fast forward to the year 2000 and OCR was made available online as a service in a cloud computing environment and in mobile applications. Since, OCR technology has been made available in internet connected mobile device applications that extract text captured using the device’s camera. Now, various commercial and open source OCR systems are available for most common writing systems, including Latin, Arabic, Hebrew, Tamil, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters.
Today’s OCR technology is far more advanced than early versions of the technology. This is because today’s advanced solutions have the ability to deliver near-perfect OCR accuracy and can be used to automate complex document-processing workflows. But, not only are the solutions much more advanced and accurate, but they’re also applicable to a far greater number of use cases. Let’s take a look at some of these in greater detail.
Optical character recognition use cases
To the modern user, OCR technology may seem like an abstract and technical concept. However, the opposite is the case and many of us encounter OCR technology in our lives on a regular basis.
On top of this, OCR services are also widely available to the public. For example, Google Cloud Vision OCR can be used to scan and store documents on any smartphone. You can even try it for free on Google Cloud.
With this in mind, let’s take a detailed look at some of the ways OCR technology is used.
Data entry
OCR is primarily used for data entry purposes. It can input data from printed paper records and business documents including passports, invoices, bank statements, and receipts.
OCR is also a common way to digitize printed text. Following OCR, documents can be electronically edited, searched, stored more compactly, displayed online, and used in machine processes such as cognitive computing and machine translation.
Vehicle registrations
OCR can also be used for automatic number plate recognition. In these instances, OCR can read a vehicle’s registration plates and identify a vehicle’s location. To do this, it can utilize existing closed-circuit television and road-rule enforcement cameras.
In these scenarios, automatic number plate recognition is used by police forces to check if a vehicle is registered or licensed. It is also used for electronic toll collection on pay-per-use roads, for parking enforcement purposes, and as a method of cataloging traffic movements.
Passport recognition
In airports, OCR technology is used for passport recognition purposes. At borders, it can be used to extract information from a passport that is placed on a scanner. This information is then scanned against third-party databases to ensure the passport is authentic, the individual is real, and the passenger is allowed to fly.
Document extraction
OCR is also often used to extract key pieces of information from documents. In lengthy documents (such as insurance documentation), it can be difficult for people to find the information they need at a glance. OCR makes it possible to find this information in an instant. In a business capacity, this leads to huge time savings and reduced admin time.
Traffic sign recognition
With traffic sign recognition technology, vehicles can recognize the traffic signs on the road ahead and alert the driver. Commonly, this technology utilizes OCR and then tells the driver about upcoming road safety features, such as a speed limit or whether they’re approaching a sharp turn or a road with restricted access.
Extracting business card details
OCR technology can also be used to extract business card information. Once information has been extracted from the business card, it can be placed into a contact list. This saves time, makes data processing easier, and creates shareable leads for sales teams.
Text scanning of printed documentation
OCR can be used to make text visualizations of printed documents. For example, OCR can be used to scan books and digitize them, turning them into eBooks. It can also turn magazines into digital media.
This technique is most popularly associated with Project Gutenberg, a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works. The world’s oldest digital library, Project Gutenberg has digitized more than 60,000 documents and made them freely available in the public domain. All digitized files can be accessed under an open format layout, which is available on almost any computer.
Converting handwritten text (pen computing)
Pen computing (the act of a computer user-interface using a pen or stylus and tablet instead of a keyboard or a mouse) is reliant on OCR technology. This is because the technology has the capacity to convert handwriting in real time.
Testing CAPTCHA anti-bot systems
Although CAPTCHA anti-bot systems have been specifically designed to beat bots, there’s some evidence that OCR can still bypass poor systems. For this reason, OCR technology is still widely used to test the robustness of CAPTCHA systems and find any weaknesses before the systems are rolled out.
Writing instructions based on CAD images
OCR technology is commonly used to write instructions based on CAD images. This means that instructions can be written in real time as a product is designed.
Converting documents to PDFs
Finally, OCR technology is also regularly used to make scanned documents searchable. This is made possible because OCR technology can convert printed documents to searchable PDFs.
Types of optical character recognition technology
Optical character recognition is generally an offline process that analyzes static documents. However, some cloud-based services do provide an online OCR API service.
Different types of OCR are available, and the four main types are:
#1 Optical character recognition
This form of OCR targets typewritten text, one glyph (purposeful mark) or character at a time.
#2 Optical word recognition
This type of OCR also targets typewritten text, but does so one word at a time. This style of OCR is particularly useful for languages that use a space as a word divider.
#3 Intelligent character recognition
By contrast, intelligent character recognition (ICR) targets handwritten printscript or cursive text one glyph or character at a time. This process usually involves machine learning, which improves accuracy.
#4 Intelligent word recognition
Similarly, intelligent word recognition (IWR) also targets handwritten printscript or cursive text, but does so one word at a time. This type of OCR is used most regularly for languages where glyphs are not separated in cursive script.
Common OCR techniques
OCR techniques vary depending on the use case and the type of OCR technology. However, most forms of OCR include techniques such as pre-processing, text recognition, and post-processing. Some also involve application-specific optimization. Let’s look at each of these techniques in greater detail.
Pre-processing
OCR software often pre-processes images. In doing so, the software improves the chances of successful recognition. A number of pre-processing techniques are used widely, but the most common options include:
- Deskewing the document to ensure proper alignment
- Despeckling the document to remove positive and negative spots
- Converting an image from color or grayscale to black-and-white in order to improve the quality of the character recognition
- Line and word detection, which establishes baseline for word and character shapes
- Layout analysis, which involves the identification of columns, paragraphs, and captions
Text recognition
When it comes to text recognition, there are two basic types of core OCR algorithm:
- Pattern matching. Here, OCR programs are fed examples of text in various fonts and formats. These are then used to compare and recognize characters in the scanned document
- Feature extraction. Here, OCR programs apply rules regarding the features of a specific letter or number to recognize characters in the scanned document. Features could include the number of angled lines, crossed lines, or curves in a character for comparison
Some pieces of software use a two-pass approach to OCR. Here, the second pass is known as ‘adaptive recognition’ and uses the letter shapes recognized with high confidence on the first pass to improve recognition of the remaining letters on the second pass. Alternatively, some modern pieces of OCR software use neural networks, which are trained to recognize whole lines of text instead of focusing on single characters.
But, the technology surrounding OCR is constantly evolving and new techniques are continually emerging. For example, iterative OCR can now automatically crop a document into sections based on the page layout. OCR is performed on the sections individually using variable character confidence level thresholds to maximize page-level OCR accuracy.
Post-processing
Post-processing can improve the accuracy of OCR. Depending on the complexity of the document, the post-processing phase may simply involve a human proof-reading and checking the document before circulating it.
The accuracy of OCR can be increased if the output is constrained by a lexicon, such as all the words in the English language or a technical lexicon for a certain field. For this reason, some pieces of OCR software use a dictionary to influence the character segmentation step and improve accuracy.
Similarly, by conducting a near-neighbor analysis during post-processing, businesses can make use of co-occurrence frequencies to correct errors. In certain industries and niches, algorithms such as the Levenshtein Distance algorithm are used in OCR post-processing to further improve results.
Application-specific optimization
The advancement of OCR technologies and techniques means that providers of optical character recognition systems have tweaked their offerings and ensured that these systems can now deal with specific types of input. This means that these systems can now take into account business rules, standard expressions, or rich information contained in color images.
Known as application oriented OCR or customized OCR, this form of optical character recognition has been applied to the scanning of license plates, invoices, screenshots, ID cards, driver licenses, and automobile manufacturing.
Prevent customers being the victim of identity verification scams with Veriff - Request a demo
If your business needs to verify customer identity documents, then our identity verification solution is perfect.
Using OCR technology, it can verify identity documents in real time and detect fake and tampered documents. It extracts barcode, MRZ, and NFC data and compares this against identity documents. Using webhooks, you can instantly receive primary data, such as the names, birthdates, document numbers, and other information on the document. It covers more than 12,000 IDs from more than 230 countries and territories and in more than 48 languages.
If you’re looking to verify customers and ensure data accuracy, then enlist the help of our biometric authentication solution. This way, you can confirm that any returning user is exactly who they’re claiming to be.
With the help of our solution, you can secure customer accounts and take a step beyond passwords and one-time passcodes. You can also make the authentication process simpler and more secure. Users can be authenticated in only a second.
If you’d like to learn more about how any of our solutions can help your business, contact our experts and arrange a free demo today.


