Blog Post
What is facial recognition?
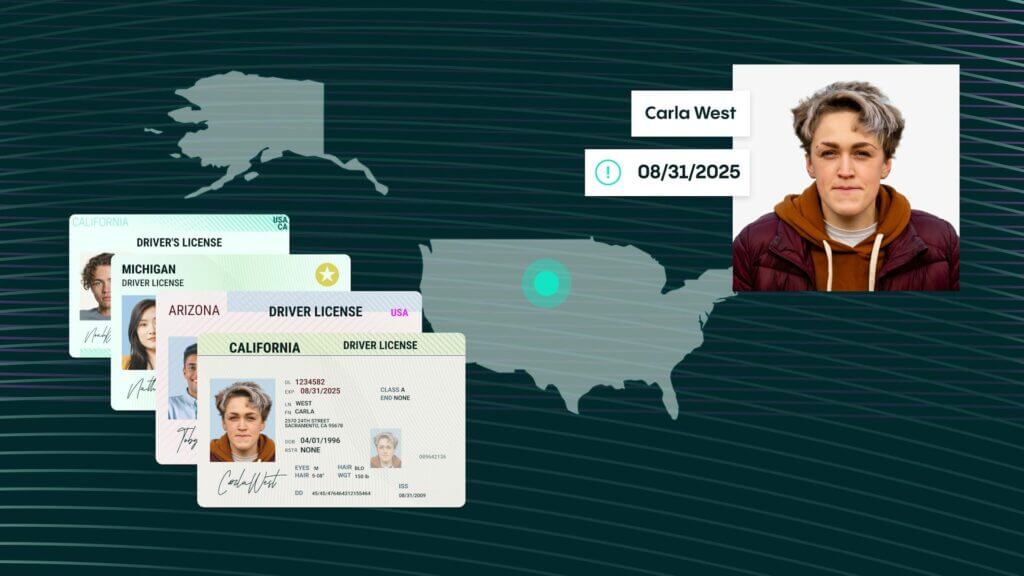
Facial recognition software has the ability to match a face in a digital image or a video with a face in a database. It does this by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image and then comparing these measurements with the measurements of photos in a database in order to find a match.
Facial recognition is a way of verifying the identity of an individual. A form of biometric identification, facial recognition uses technology to identify and recognize a human face.
Facial recognition systems are pieces of technology that are capable of matching a human face to a particular face within a database, or to a stored image of a particular user’s face.
To do this, a facial recognition camera will measure the facial features present within a given image. The data points measured include the distance between the eyes and the distance from the forehead to the chin. It will then compare this data to either the stored image or a database of images in order to find a match.
Although a relatively new form of technology, facial recognition is now incredibly popular and is used widely. A Georgetown University study suggests that half of all American adults have their images stored in one or more facial recognition databases that law enforcement agencies can search.
What is facial recognition used for?
Most people now use one particular form of facial recognition in their everyday lives. This is because Apple’s Face ID feature is used to unlock newer versions of the iPhone. Not only does the Face ID feature allow users to access their phone quickly and easily, but it’s also highly secure. Apple claims that the chance of a random face unlocking your phone is about one in one million.
Although facial recognition is most widely used for user verification purposes, it’s also used prominently in a number of other instances. For example, facial uses of facial recognition include:
- Law enforcement purposes
- At airports and border control
- Finding missing persons
- Improving the retail experience
- Online and app-based banking
- Marketing and advertising
- Healthcare
- Tracking the attendance of workers or students
- Recognizing drivers
- Monitoring gambling addictions
Examples of facial recognition technology
As you can see from the above, facial recognition technology is incredibly useful in a wide variety of situations. With this in mind, let’s look at how the technology is used practically.
Amazon
Back in 2016, Amazon began to promote a cloud-based facial recognition service called Rekognition.
Today, Rekognition is used for content moderation, celebrity recognition, and identity verification. The software is also used by a number of United States government agencies, including US Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and police.
British Airways
British Airways uses facial recognition technology to verify the identity of passengers in the US. Travelers’ faces are scanned by a camera before they board the plane. As a result, the traveler does not need to show their passport or boarding pass.
The airline has been using the technology on UK domestic flights from Heathrow and is working towards biometric boarding on international flights from the airport.
Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola has used facial recognition in several different ways over the years. For example, the company has used the technology to reward some of its customers in China for recycling at its vending machines. In Australia, the company has used the same technology to display personalized ads.
Facebook began using facial recognition technology in the US in 2010. Back then, it automatically tagged Facebook users in photos using its tag suggestion tool. However, since 2019, the company has made the feature optional as part of its drive to become more privacy-focused.
Snapchat
Snapchat is a pioneer in the field of facial recognition technology. The social media giant allows brands and organizations to create filters that mold to each user’s face.
History of facial recognition
The history of facial recognition technology can be traced back to the 1960s. This is when mathematician and computer scientist Woodrow Wilson Bledsoe first developed a system of measurements that could be used to put photos of faces in different classifications.
Woodrow Wilson Bledsoe’s work soon caught the eye of law enforcement agencies. Between the 1970s and the 1990s, many agencies sought his advice and developed their own facial recognition systems. Of course, these were primitive compared to the systems we use today, but they did pave the way for innovations that followed.
Following this, 2001 was a landmark year for facial recognition technology. This is because, at that year’s edition of the Super Bowl, law enforcement officials used facial recognition technology to help identify people in the crowd for the first time.
However, it took another decade until computers became powerful enough and fast enough for facial recognition software to become a standard feature. At this point, American police began to use facial recognition to identify suspects and those who participated in protests. Around this time, facial recognition software was also used to identify Osama bin Laden.
Fast forward another four years to 2015 and facial technology really hit the mainstream, as Windows and Android began to allow users to log into their devices using their faces. Apple then followed suit with Face ID in 2017.
Ever since, more and more companies have begun to harness the power of facial recognition. However, that said, in recent years we have witnessed controversy over the use of technology. For example, some cities have banned governments from using facial recognition, such as San Francisco, Oakland, and Boston.
Similarly, after Black Lives Matter protests in 2020, several tech giants, including Amazon, Microsoft, and IBM, announced that they would no longer sell their facial recognition technology to law enforcement agencies.
Is facial recognition legal?
Yes, facial recognition is legal. This is why it’s used in a number of different industries and for so many different purposes.
That said, in the last couple of years, around two dozen states have passed laws restricting the technology due to facial recognition security concerns as well as worries about the accuracy of the technology. On top of this, as we mentioned above, some vendors will not sell facial recognition technology to the police and law enforcement agencies.
How does facial recognition work?
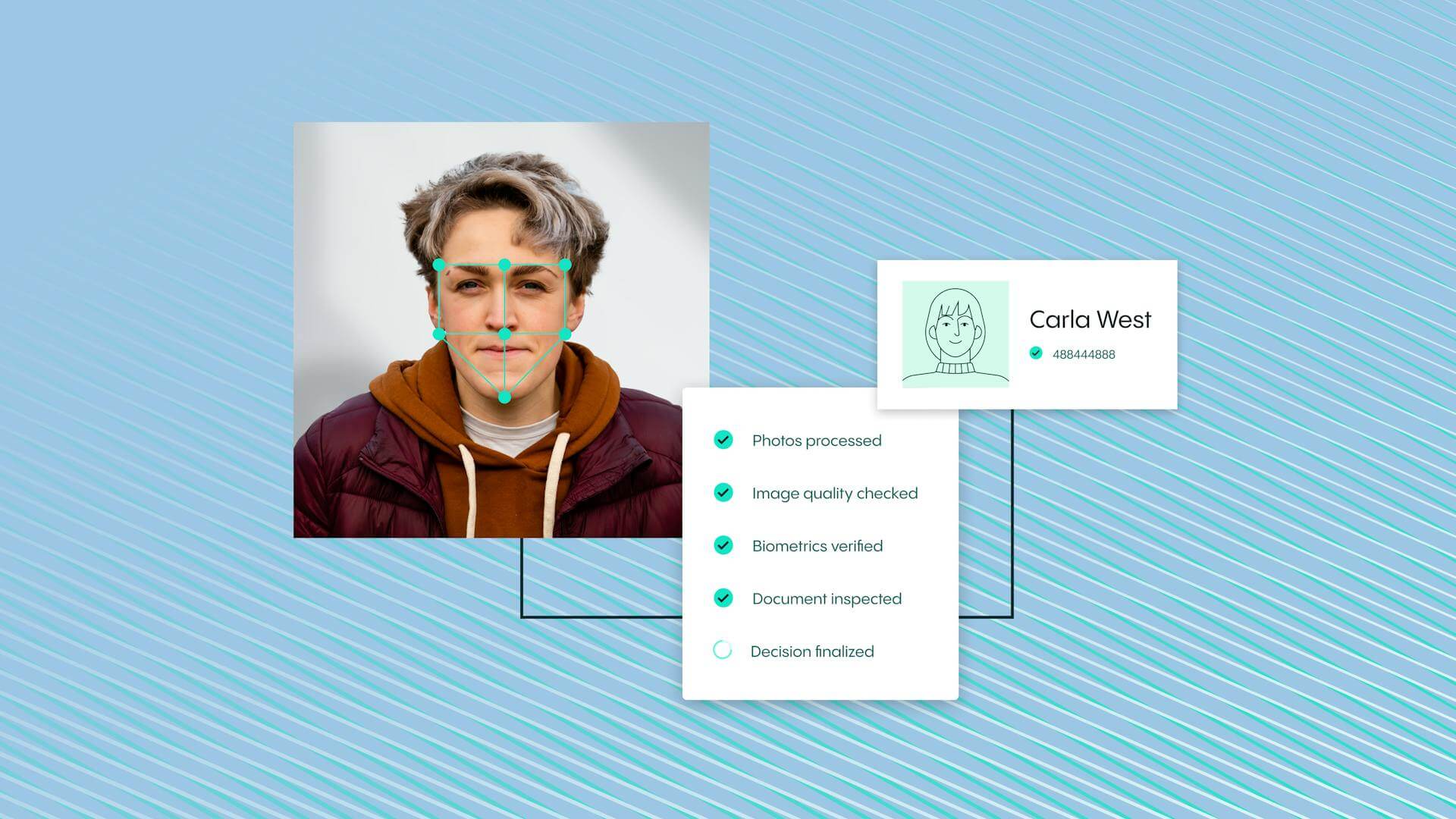
Exactly how facial recognition works depends on the technology used and the purpose for carrying out the process. However, broadly speaking, facial recognition technology follows this four-step process:
- Step 1: A picture of the user’s face is captured from a photo or a video. This may be from a photo or a video that a police force has access to already (such as CCTV footage), or a photo or video that the user takes themselves (if they’re trying to access their phone or an online account)
- Step 2: A piece of facial recognition software then reads the geometry of your face. In identifying all of your facial landmarks, these pieces of software create a facial signature (which is essentially a mathematical formula) that’s unique to you. The facial scanning process is quick and only takes around a second
- Step 3: Your facial signature is then compared to a database of known faces. These databases are vast. For example, in America, it’s estimated that at least 117 million citizens have their faces on at least one police database. The FBI also has access to more than 500 million facial images for searches
- Step 4: A match is found between your facial signature and a face in the database
Of course, when it’s used for verification purposes, facial recognition follows a slightly different process. This is because, instead of relying on a vast database of photos to determine an identity, the software instead identifies and recognizes one person as the sole owner of the device or account. To do this, it compares the photo submitted by the user with a previously-saved image and facial signature. If a match is found, access is granted. This process is also followed by Face ID, which works with a live image rather than a submitted selfie.
What is facial recognition software?
Facial recognition software (also known as a facial recognition system) is a piece of technology that aids the facial recognition process.
Facial recognition software has the ability to match a face in a digital image or a video with a face in a database. It does this by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image and then comparing these measurements with the measurements of photos in a database in order to find a match.
Facial recognition software is most commonly used in the ID verification services industry, where it verifies the identity of a user before that individual is allowed to access their account. In these instances, it is often a vital part of ensuring a firm’s AML compliance and KYC compliance processes.
What type of data does facial recognition use?
Facial recognition software uses biometrics to map facial features from a photograph or video.
During the process, facial recognition software uses computer-generated filters to transform face images into numerical expressions that can be compared to determine their similarity. These filters are usually generated by using deep learning, which uses artificial neural networks to process data.
How long does facial recognition take?
One of the main benefits of facial technology is that it’s incredibly quick. In fact, our facial recognition process can verify the identity of any user in less than a second. This means that users are given almost immediate access to their accounts.
The same can be said for smartphone users, who can access their phones much quicker with Face ID than they can by entering a passcode.
How accurate is facial recognition?
Although critics say that facial recognition can potentially lead to false identifications, facial recognition operates with a high degree of accuracy. For example, our biometric authentication solution is 99.99% accurate.
Plus, studies show that facial recognition software has become increasingly accurate over time. For example, tests conducted by the National Institute of Standards and Technology in 2014 showed that the best face identification algorithm available had an error rate of 4.1%. In 2020, a repeat test showed this error rate had dropped to 0.08%.
That said, it’s important to state that accuracy is higher when identification algorithms are used to match people to clear, static images, such as passport photos. Used in this context (which is exactly how we use biometric authentication), accuracy scores on the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Facial Recognition Vendor Test regularly reach almost 100%.
By contrast, accuracy rates are much lower when identification algorithms are used in the real world. For example, the Facial Recognition Vendor Test found that the error rate for one algorithm rose from 0.1% when faces were matched against high-quality mugshots to 9.3% when matched to pictures of individuals captured in public. Error rates rose especially when subjects were not looking directly at the camera or were partially hidden by shadows or objects.
Advantages of facial recognition
Depending on the context in which it’s used, facial recognition technology can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Finding missing people: With the help of facial recognition, law enforcement agencies have been able to track down missing persons and suspects in crimes
- Security of accounts: Facial recognition is also incredibly useful for securing phones and online accounts. The accuracy of the technology and the ease of use means that facial recognition is much better for both the business and the customer than using passwords, which can be lost, stolen, or forgotten
- Making flying safer: Airports across the globe are using facial recognition to identify criminals and potential threats as they enter airports. This way, they can be stopped before they attempt to board a flight
- Making shopping easier: Retailers are also now using facial recognition technology to improve the shopping experience. Instead of forcing customers to pay with cash or credit, retailers can use facial recognition to immediately charge purchases to their accounts. Similarly, this technology can also be used to serve customers with personalized ads and offers
Disadvantages of facial recognition
Although facial recognition software provides many advantages, there are also associated disadvantages, including:
- Privacy threats: Some critics argue that facial recognition is a threat to privacy. This is because an individual may have their face saved in a police database without their permission. However, many private companies (such as Facebook) have overcome this issue by allowing users to opt out of the process
- Cases of mistaken identity: Although the accuracy of facial recognition technology has improved massively over the past decade, the technology still isn’t perfect. This can potentially lead to instances of mistaken identity
- It can be tricked: Criminals can trick facial recognition by wearing masks or facial disguises
- Factors limiting effectiveness: Studies have found that as people age, their features change. Due to this, facial recognition has an increasingly difficult time identifying them. Other studies have shown that facial recognition is less effective in identifying people of color, and women. However, as we pointed out earlier, the technology is constantly improving and is becoming increasingly accurate
The future of facial recognition
Looking to the future, there’s no doubt that the technology behind facial recognition will continue to improve. In the coming years, thanks to facial recognition, we can expect access controls to be more frictionless, fast, and multifaceted.
One great example of this is in the workplace. Today, the vast majority of buildings are secured via magnetic cards or badges, which can be stolen, lost, or manipulated. Soon, facial recognition technologies will alleviate these concerns, while also allowing employees to access these spaces with as little friction as possible.
In non-business settings, we can also see how this technology could be used to protect the home. However, the technology is capable of going one step further if new developments are made. For example, facial recognition technology can be integrated with home-centered applications. It could also announce guests and provide remote access when required.
Similarly, facial recognition technology could also be used to replace tickets for sports events, concerts, and public transport. If applied correctly, the technology could even replace car keys.
No matter how it’s applied, facial recognition technology appears to be the future of security.
How facial recognition can help your business
As we’ve shown, facial recognition software can help businesses around the globe. This is because this technology can help secure user accounts, improve user access, and speed up the authentication process.
Our biometric authentication solution is one of the best pieces of facial recognition software available on the market. It can authenticate any user’s identity in just one second. Plus, the technology is 100% automated and 99.99% accurate. Added to this, it authenticates 99% of users on their first attempt.
If you’d like to discover more about how our facial recognition technology can help your business, talk to our experts today.