Blog Post
How face identification can be used for business
In today’s world, the vast majority of people use some form of facial recognition technology every day. From unlocking our phones to signing into banking apps or passing through airport security, we’re all used to using our faces to gain access to systems or verify our identity.
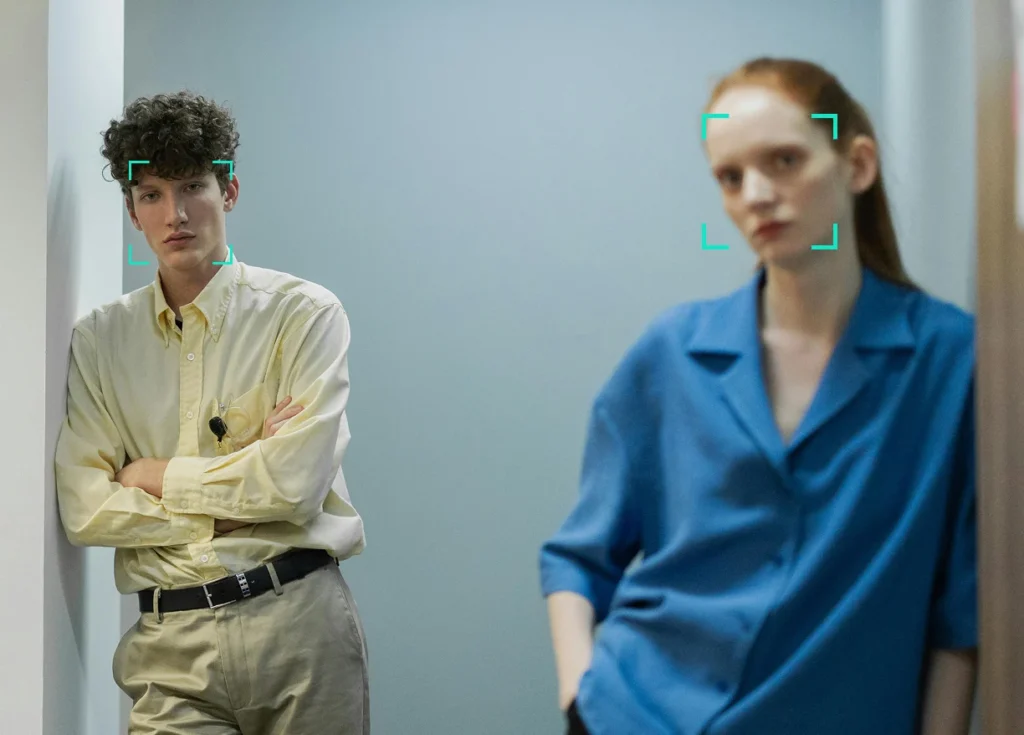
Facial recognition technology can help your business identify or verify an individual’s identity using a scan or a photo of their face. This process is most commonly carried out using a photo the individual submits. However, faces can be identified within crowd/CCTV shots and from videos.
Facial recognition is a category of biometric security. Other forms of biometric software include voice recognition, fingerprint recognition, and iris recognition. Face identification software is usually associated with security and law enforcement. However, although face identification is undoubtedly useful from a security perspective, the technology can also be used by businesses to improve retail experiences, ensure compliance with anti-money laundering regulations, and to track worker attendance.
With this in mind, let’s take a detailed look at how face identification can be used for businesses. But, let’s first start by looking at the rise of facial identification and authentication, as well as popular use cases for the technology today.
The rise of facial identification and authentication
The development of ID verification systems began in the 1960s, when computer applications were developed that could pinpoint and measure facial features on a given image.
These early facial recognition applications were known as ‘man-machine applications’ because the coordinates of the facial features in a photograph first had to be established by a human.
As part of this process, humans would pinpoint the coordinates of facial features such as the pupil centers and the inside and outside corner of eyes on a graphics tablet. A computer would then automatically compare the distances for each photograph, calculate the difference between the distances, and return the closed records as a possible match.
Almost a decade later, Takeo Kanade developed a system that did not require any human intervention. However, testing on his system later proved that it was not always reliable. In fact, even when the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) and the Army Research Laboratory (ARL) established the face recognition technology program FERET to develop automatic face recognition capabilities in the 1990s, doubts over accuracy remained.
However, by this point, testing on face identification was becoming more common and systems were improving. As a result, following additional testing in 1993, the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) offices in West Virginia and New Mexico became the first DMV offices to use automated facial recognition systems as a way to prevent and detect people obtaining multiple driving licenses under different names.
Following this, the use of facial identification methods then expanded during the 1990s. Throughout the decade, the technology behind the systems improved rapidly, and systems were developed using a variety of new methods, such as the Eigenface method (also known as the PCA method) and the Bochum system. Both of these made face matching technology faster and more reliable.
Fast forward to the 2000s and real-time face detection became possible for the first time. This expanded the use cases for face detection and caused more companies to invest in the technology.
In the past decade, engineers have reached agreement that a Convolutional Neural Network is the best way to perform facial detection. Since agreement was reached on this point, engineers have been able to prove that computers can consistently beat humans at recognizing faces. As a result of the technology becoming more reliable, we’ve also seen a boom in use cases.
Facial recognition use cases
In today’s world, the vast majority of people use some form of facial recognition technology every day. From unlocking our phones to signing into banking apps or passing through airport security, we’re all used to using our faces to gain access to systems or verify our identity. With this in mind, here are the top use cases for face identification.
Unlocking phones and accessing apps
Apple’s Face ID technology brought biometric identification to the masses. Now, nearly all smartphones use a facial identification solution for unlocking purposes, rather than a passcode or a password. Many apps that hold sensitive information (such as banking apps) also do the same.
This is because biometric Face ID technology offers a powerful way to protect personal identification from fraudsters. If a user’s phone is stolen or their usual passwords are compromised, facial identification methods mean that sensitive data remains inaccessible.
On top of this, face identification technology is incredibly secure because faces are unique. Apple claims that the chance of a random face unlocking your phone is about one in a million.
Law enforcement
Throughout the US, facial recognition technology is used by law enforcement agencies. Commonly, this includes police officers collecting mugshots from suspects and then comparing this image against local, state, and federal face recognition databases. Once a suspect’s photo has been taken, their picture will be added to databases and will be scanned whenever police carry out another criminal search.
That said, law enforcement agencies also use face identification techniques to identify people in CCTV images or to identify suspects. Similarly, facial recognition technology is also used by law enforcement officials to find missing persons and identify victims of human trafficking. If a missing individual is on a database, then law enforcement can be alerted as soon as they are recognized by face recognition technology at an airport, in a retail store, or in a public space.
At airports and border control
Facial recognition technology is also now a regular sight at airports. The creation of biometric passports means that passengers can skip the long queues at passport control and can instead walk through an e-passport control gate. Not only do these gates increase convenience for passengers, but they also increase security by eliminating human error.
By next year, it’s estimated that facial recognition technology will be used by 97% of travelers. Plus, in the coming years, it’s also thought similar pieces of technology will be used to enhance security at large sporting events and concerts.
Reducing retail crime
Store owners can also use facial recognition technology to reduce retail crime. This is because the technology can be used to identify when known shoplifters, organized retail criminals, or people with a history of fraud enter stores. Photographs of individuals can be matched against large databases of criminals so that loss prevention and retail security professionals can be notified when shoppers who potentially represent a threat arrive.
Improving the retail experience
In a retail setting, face recognition technology can also be used to improve a customer’s experience. Although this technology is not widely available yet, experts believe that in the next couple of years Face ID could be used to recognize customers, make product suggestions based on their purchase history, and point them in the right direction in the store. Once the customer has made their selections, they could then use biometric authentication for payment and skip any lengthy queues.
Financial services
In the world of financial services, face identification technology can be used to verify customer identities, enable transactions, and secure customer data.
By lessening reliance on passcodes and passwords, banks and financial service providers can create secure systems and lock out criminals. Plus, by adding verification and biometric face ID processes during onboarding, financial institutions can also ensure that they meet all KYC and AML obligations.
When banks put facial recognition and identification processes in place, there are no passwords for hackers to compromise. Plus, if a hacker steals their photo database, then liveness detection (a technique used to determine whether the source of a biometric sample is a live human being or a fake representation) will prevent them from using it for impersonation purposes.
Healthcare
In hospitals and healthcare settings, biometric authentication methods are used to help with patient care. This is because facial recognition can be used to access patient records, streamline patient registration, detect emotion and pain in patients, and even help to identify specific genetic diseases. On top of this, some companies are even developing apps that use facial recognition to ensure that people take their medication as prescribed.
Tracking student or worker attendance
Some educational institutions in China are using face recognition technology to ensure that students are not skipping classes. This technology also prevents registers from being doctored, or for one student to sign in on another’s behalf.
This technology is now also being used in some workplaces, where employers can track employee attendance in real time. This technology is particularly important in workplaces where sensitive information is stored. If access to these storage areas is controlled by face recognition, then employers can gain accurate information about who has accessed the room and when.
Monitoring gambling addictions
Finally, facial recognition technology can also be used by gambling companies to help protect customers and ensure compliance. Human staff members struggle to monitor and notice those who are moving around the casino. However, facial technology can monitor every movement on a crowded casino floor.
As a result, it can be used to help staff members identify those who are registered as gambling addicts or those who are on self-exclusion lists. As well as helping these individuals, the technology can also help the casino operator, who will face hefty fines if they are found to have allowed those on self-exclusion lists to continue gambling.
Phases of face identification for businesses
So, now we have a good understanding about how to use biometric authentication and how this technology can be used to enhance the customer experience, bolster security, and improve convenience. Now, let’s look at how the technology works in practice.
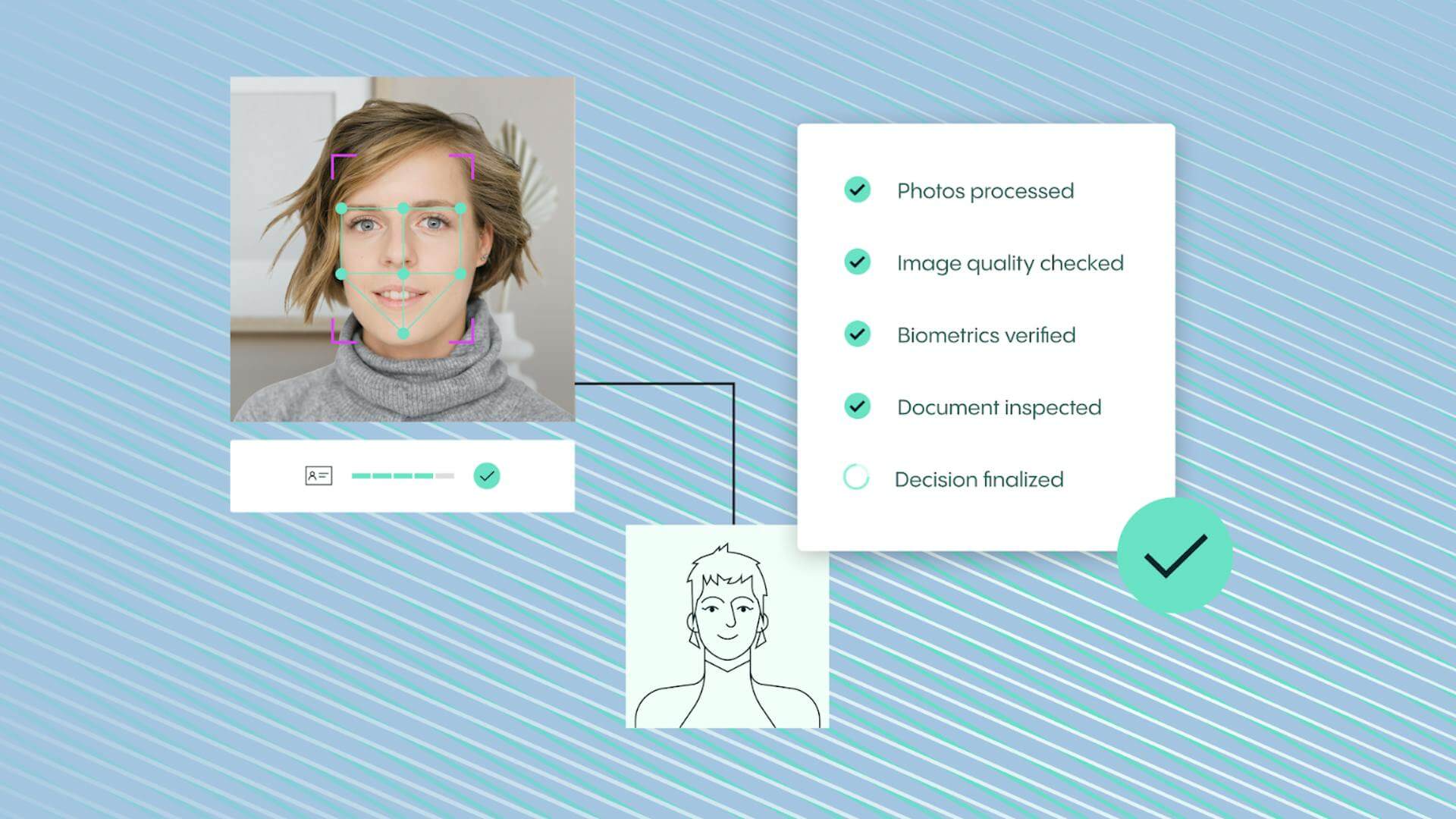
Although the facial identification process is simple for users and takes place in a matter of seconds, it’s actually a relatively complex multi-step procedure that involves several specialized sub-systems. The process involves the following four stages:
Detection and tracking
This is a pre-processing stage that is responsible for identifying and tracking faces that are present in an image or video file. In basic terms, once the detection and tracking phase of the process has been completed, we can be certain that there’s a face in the video or photo that can be processed further.
On a more complex level, the detection and tracking phase of face identification is also responsible for tracking certain features or expressions in a face, should that be needed.
Alignment
Next comes the alignment phase. Faces in a given image or video may not follow any particular guidelines. Take CCTV imagery in a clothes store, for example. In a CCTV video/still, a customer may be close to the camera, peeking out from behind a clothes rail, looking in the mirror, standing in profile, or standing right in the back of the image waiting for space in the changing rooms. In these scenarios, face detection is even harder. Thankfully, the alignment process can be used to tell us where the face is and the contours of the facial features.
Of course, if the customer provides a selfie for identity verification purposes or allows somebody to take their picture, such as at the airport gates as part of passport control measures, the alignment phase of the face identification process is less important. That said, it can still be used to ensure that the photo the individual has submitted meets any given requirements. For example, it can ensure that somebody isn’t standing too far away from the screen, or that their entire face is present.
Facial feature extraction
Much like the name of this process suggests, feature extraction involves the individual features of the user’s face being extracted from the image. The facial recognition technology typically identifies the following data points:
- Distance between the eyes
- Distance from the forehead to the chin
- Distance between the nose and mouth
- Shape of the cheekbones
- Contour of the lips, ears, and, chin
The system converts the face recognition data into a string of numbers or points called a faceprint. Each person has a unique faceprint, similar to a fingerprint. The information used by facial recognition can also be used in reverse to digitally reconstruct a person’s face.
At the conclusion of this stage, the computer has collected enough complex data to tell a face apart uniquely.
Feature matching and classification
In this final stage of the process, the inputs received from feature extraction are matched against the given database to deduce the person’s identity. This phase is also known as a classification phase because the algorithm may be needed to categorize faces instead of individually identifying them.
How Veriff supports you with biometric face identification
Our biometric authentication solution can help you go passwordless and secure accounts easily.
We believe that facial biometrics enables the simplest, most secure authentication experience. With the help of our solution, you can authenticate any user’s identity in only one second, using just a selfie. The process is 100% automated and 99.99% accurate. Plus, 99% of users are authenticated on their first try thanks to assisted image capture.
Our biometric authentication solution confirms a returning user is exactly who they’re claiming to be. As a result, it mitigates fraudulent activities such as account takeover and identity theft. To do this, it asks the user for a selfie that it can use for biometric identification.
Once the user submits their selfie, the image is then checked for liveness and realness in real time. When the solution has confirmed the image is live and real, the selfie is then compared to a previously verified face and identity. An authentication decision is reached in about a second and the user is informed immediately.
See how Veriff’s biometric authentication solutions can help you – Book a demo
No matter what industry you operate in, our biometric authentication solution can help you. Whether you need to secure accounts, ditch legacy technologies, or automate identification processes, we can help.
To find out how, book a personalized demo with our expert team today. We’d love to explain exactly how our class-leading solution can meet your needs.